With the increased complexity of modern IT environments, organizations' cyber exposures have become more challenging to handle, leaving critical cracks and gaps in organizations' digital armor. This places pressure on traditional vulnerability management programs, which, by nature, focus only on known software, system, and application vulnerabilities.
To address this demand, organizations adopt a more comprehensive and revolutionary approach known as Exposure Management, or Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), as coined by Gartner®. 2024 Gartner® Hype Cycle™ for Security Operations states that the CTEM program enables organizations to regularly assess the visibility of their digital assets and verify how accessible and exploitable they are [1].
In this blog, we will define the core steps of an Exposure Management program, highlight its benefits, and share best practices to guide you in adopting the exposure management lifecycle.
What Is Exposure Management?
Exposure management is a continuous cybersecurity approach that focuses on identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and addressing security risks across exploitable IT assets. It helps organizations reduce risk by validating exposures and mobilizing appropriate actions to improve their overall security posture.
Gartner introduces the core lifecycle of a Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) program, explaining the key steps and corresponding tools that support this program.
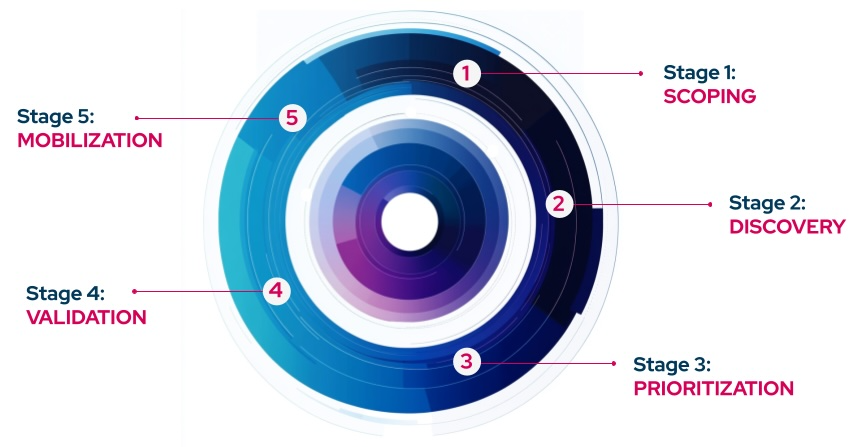
Figure 2. Five Steps of Continuous Threat Exposure Management Lifecycle: Scoping, Discovery, Prioritization, Validation, and Mobilization
We will start with step one, scoping.
CTEM Step 1: Scoping
Scoping is how an organization defines what areas or risks it wishes to assess and test within its Exposure Management process. As noted in Gartner's 2024 Strategic Roadmap for Managing Threat Exposure, scoping should be adaptable and focus on the most appropriate areas for the organization based on its risk profile.
The following solutions enable the scoping stage of Exposure Management:
In addition to these core tools, other technologies can enhance the scoping process, such as:
After the scope is defined, it is time for the discovery step.
CTEM Step 2: Discovery
Discovery involves identifying an organization's potential cyber exposures. This phase's most notable tools are the Vulnerability Assessment (VA) tools.
According to Gartner, VA technologies have now been subsumed into Exposure Assessment Platforms, or EAPs, which provide a more holistic and consolidated view of organizational risk through a combination of multiple data sources.
CTEM Step 3: Prioritization
For the prioritization phase, Gartner's Hype Cycle for Security Operations, 2024 introduces Vulnerability Prioritization Technologies (VPT), now subsumed into Exposure Assessment Platforms (EAPs).
These tools aim to rank vulnerabilities based on factors such as CVSS scores, asset criticality, business impact, etc. However, Gartner also highlights that organizations that only rely on such factors for prioritization are missing the real benefits of EAPs. This is because the Vulnerability Prioritization Technologies alone don't have any insights into the exploitability of vulnerabilities within an organization's unique environment, resulting in unmanageably large amounts of exposures without any insight into which poses a real threat to the organization.
To fill this gap, Adversarial Exposure Validation solutions are used to validate actionable exposures, to prevent wasting time on theoretical ones. These tools are both used for better prioritization, to get the most of Exposure Assessment Platforms (EAPs). The tools used here are also listed under the next step, Validation.
CTEM Step 4: Validation
As stressed in the previous step, the primary motivation behind the validation phase is to identify, out of thousands of possible exposures, the ones that matter to the organization and, therefore, require immediate remediation efforts. By running realistic attack simulations, these technologies demonstrate which exposures could be exploited in a real life attack campaign by an adversary to breach the organization.
The following tools and technologies are now subsumed under Exposure Validation technologies to support the validation phase of Exposure Management:
These technologies drastically improve the prioritization of exposures and reduce the operational burden on mobilization teams by pinpointing the most critical threats.
CTEM Step 5: Mobilization
Mobilization is the last stage of Exposure Management, wherein the remediation teams are mobilized to deal with the exposures that have been validated effectively. Once validated, the exposures are scored on criticality. Based on criticality score evaluation, remediation work is segregated and distributed among different teams. For instance, while team A is responsible for remediating the exposures with a criticality score of 8-10, team B might be responsible for 5-7, which can be facilitated by ticketing and workflow tools.
Besides the human factor in remediation processes, security vendors such as Picus also provide ready-to-deploy mitigation suggestions that simplify the mobilization process by minimizing complex, intrusive patches. Mitigation suggestions from several security control vendors will drive teams to rapid and effective remediation.
Benefits of Exposure Management
Following are three key benefits of running a successful exposure management program.
-
Proactive Risk Management: Exposure management is how an organization continuously identifies and validates its vulnerabilities, prioritized by the actual risks they pose, to address potential threats before they can be exploited. This will, in turn, reduce breaches and strengthen the overall security posture.
-
Resource Efficiency: Not all vulnerabilities are created equal, so the saying goes. Seriously, though, exposure management programs help focus resources for security teams on the most critical threats by validating which vulnerabilities are truly exploitable.
For example, a vulnerability scored at an initial 9/10 in terms of severity may be downgraded to 3/10 based on validation that existing compensating controls have been operating effectively and mitigating most of the associated risks. This shift in risk score significantly changes the SLA in terms of the mobilization timeline; whereas a vulnerability rated at 9/10 may call for immediate action translation within 24 hours, one rated at 3/10 gives a 3-week response window. This approach helps avoid wasting resources on lower priority issues, allowing for more efficient use of time and effort.
Best Practices for Exposure Management
Here are the four best practices for continuous threat exposure management.
With continuous Exposure Assessment embedded in your security operations, monitor the entire digital environment not just high-risk assets, for example, internet-facing servers. This proactive approach finds hidden vulnerabilities across all assets, not just high risk ones, allowing for early detection and timely remediation, hence strengthening overall resilience.
We know it is a rather overused cliché, but the fact is that the cyber threat landscape indeed keeps evolving and improving. If one must prevail, exposure assessment should be an ongoing process in updating the defenses to meet the new threats. What is paramount here is that this shift in perspective moves security efforts from just being reactive one-off fixes to actually building a long-term proactive exposure management strategy.
After analysis, validation is necessarily required in order to weed out theoretical risks. Adversarial exposure validation shows if the identified vulnerabilities can actually be exploited in your specific environment. This ensures that security efforts focus on real, immediate threats so that resources are not wasted on low-risk issues that don't call for urgent action.
When it’s time to mobilize, the focus should be on vulnerabilities that are both critical and confirmed as exploitable. Group your mobilization efforts based on the actual risk each exposure poses, and assign appropriate SLAs for each group. This way, you’re not wasting resources on low-priority issues, and your security teams can concentrate on tackling the most urgent, high-impact threats first.
Conclusion
There are no shortcuts in Exposure Management. While it is of utmost importance that the identification and prioritization of vulnerabilities be grounded on exposure assessment, equally important is the fact that validation must confirm which of those identified vulnerabilities pose a real, exploitable threat. If not, then organizations will waste so much time and resources on theoretical risks while the actual, immediate dangers lurk within their systems.
Coupling Exposure Assessment Platforms (EAPs) with Adversarial Exposure Validation technologies enables security teams to move from a reactive stance overwhelmed by the tide of vulnerabilities to a proactive, strategic one directed at the most critical risks. This is a careful balance between maximizing resource efficiency and ensuring mobilization efforts are concentrated in their effect, creating genuine resilience for the organization against cyber threats.
It is a methodology that really underlines the formula for successful exposure management, assessment, and validation in line with transforming raw data into insights that ensure actionable outcomes. It ensures a robust, targeted, resilient security posture tested against real-world threats.

-3.png?width=353&height=200&name=image%20(79)-3.png)





.png?width=353&height=200&name=what-is-exposure-assessment-blog-preview%20(1).png)
